Feet are commonly considered a taboo subject. Most people would rather not speak about their feet, or the problems they may have inside their shoes. This phobia has led to limited information on the topic, until now. But let’s face it — we rely on our feet everyday to get us around and do the things we do. We might not think too much about them until they start to hurt and hinder us from carrying out our daily responsibilities.
From itching between the toes and callused soles to more serious bunion and ankle problems we have compiled a glossary of the most common podiatry ailments with some other useful information regarding foot pain.
What causes foot pain?
Foot pain can result from a variety of reasons such as trauma, injuries, disability, disease or neglect, even wearing the wrong type of shoes for your foot type or size for an extended period of time can cause you to suffer debilitating foot pain and discomfort. If you are experiencing any type of foot pain for an extended period of time, it is a sign from your body that medical help is required.
To diagnose any sort of foot pain, first you will have to determine what the problem is first and then find a possible solution or treatment plan. For example, does it hurt for you to walk on a day-to-day basis, is there a dull ache, is the pain piercing or sore? Is the pain affected by weight bearing or can you still feel pain non weight bearing? Seeing a Podiatrist is the best way to diagnose foot pain efficiently and get the necessary treatment(s) and advice as quickly as possible.
What kind of foot pains are there?
Experiencing trouble with your feet and not sure exactly what it is or why you are getting these pains? We have put together a quick guide on the different types of ailments, their causes, and how to prevent and treat them.
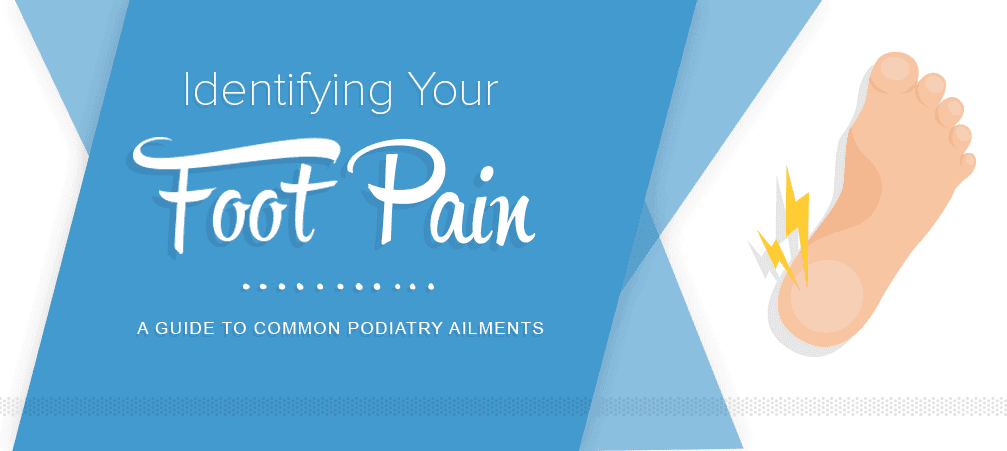
Achilles Tendonitis
Describing pain, inflammation, impaired performance and degeneration of the tendon, Achilles Tendonitis is a common injury among athletes. Activities such as jumping, changing from soft to hard surfaces and immediate intensity boots can be the causes. Pain generally occurs within the calf and heel during running, pointing of the toes or taking the first few steps in the morning. Minimizing the pain can be as easy as resting, icing and taking an over the counter pain reliever. Remember to stretch before exercising and warm up properly.
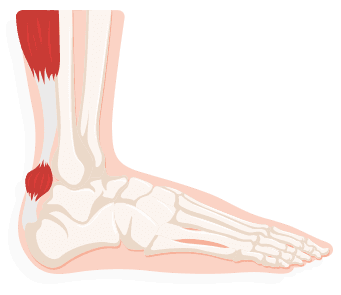
Arch Pain
Arches in the feet can vary. Arch height can be an important factor in whether or not an individual will experience arch pain. People who are Flat-footed tend to experience fatigue and loss of strength in tendons, muscles and the ankles. Those with high arches generally have more pain in their heels, forefoot and lower backs with an increased risk for leg injury due to lack of the mid foot structural imbalance and support and more pressure forced upon the heel and toes. Pain can decrease or be completely alleviated from shoe insoles (orthotics) or specialty made footware, avoid wearing high heels.
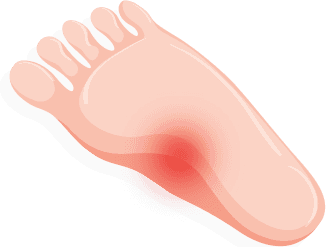
Bunions
A bunion develops when the big toe turns inwards towards the second toe. It can develop into a small fluid filled pouch at the side of the joint at the base of a big toe. Common causes include hereditary influence, small or high heeled pumps and gender, as women are more likely to suffer from bunions than men. Relief from bunions includes different footwear with a wider and a deeper toe box, padding, pain medication, and ice. If bunions continue to grow, injections and surgery may be necessary.
Calluses
When skin is rubbed continually in a localized area, the body begins to increase the skin layers to protect the location under pressure. Calluses are the extra padding, generally on feet because of shoes that are either too tight or too loose and causing an unnatural sheering forces upon the parts of the foot, or because of disease or deformity of foot inside the shoe . Generally, there is nothing to be concerned about with calluses as they are not painful or unhealthy. However, in some instances calloused skin needs to be reduced as not to put too much pressure on the underlying bones of the foot beneath the callus. Often the biggest frustration is physical appearance, though treatment can include orthotics, padding, changing footwear and rubbing off the extra skin with a pumice stone. If the feet have calluses and corns or if the situation begins to get serious, surgery may be considered.
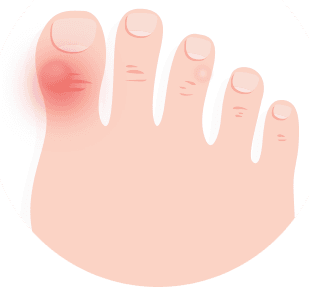
Claw Toes
When your toes point up or down and can’t straighten, at the middle and end joints in the toe, this can lead to severe pressure and pain. Ligaments and tendons tighten causing the toe's joints to curl downwards. Usually, this is a result from nerve damage caused by diseases like alcoholism, diabetes, disability, arthritis, or a stroke. Without proper footwear, you may get foot irritation and calluses easily. To avoid this, wearing insoles and Physical therapy will help. High heels and tight shoes should not be worn frequently. Surgery is also available for severe conditions.
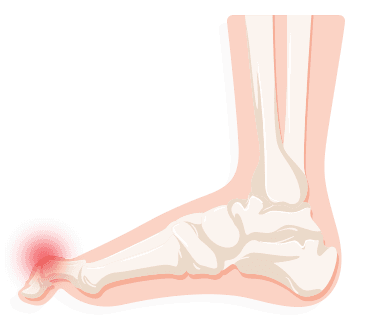
Gout
A serious form of arthritis, gout affects more than 2 million Americans. Sharp pain, sudden tenderness and increasing inflammation are common symptoms. Generally infrequent and short lasting, gout can become much more serious and life altering. Men are more likely to have gout as are alcoholics, obese people, diabetics and those with a genetic line of sufferers. Diagnosed through a urine, blood or fluid sample, gout can be relieved through anti-inflammatory drugs and injections. Staying hydrated, away from alcohol, limiting meat proteins and maintaining a healthy body weight all can reduce the risk of gout.
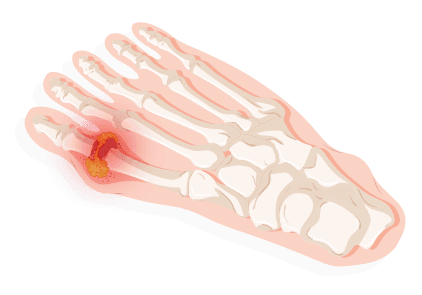
Hammer Toes
An uncomfortable and unattractive condition, hammer toes occur when a middle toe joint causes your toe to bend or curl downward instead of pointing forward. This deformity can affect any toe on your foot although it mostly affects the second or third toe. Known to be painful, hammer toes are best treated as quickly as possible. Causes include poor footwear, arthritis, high arches in foot and toe injuries . Genetics and consistent bunions can be warning signs. Splinting, changing footwear, padding the toe and creams can all be used. If ineffective, surgery may be necessary.
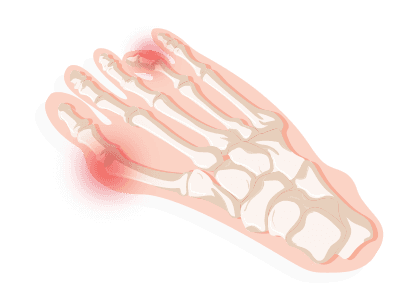
Heel Fractures
If you’ve recently gotten out of a bad car accident or suffered from any high-impact injury, you may experience a heel fracture. Symptoms of this include heel pain, swelling, trouble walking, and bruising. Medical attention is highly recommended if you think you might have any degree of heel fracture. Physical therapy may also help alleviate the pain and improve the condition. In the meantime, doctors may prescribe over-the-counter or prescription pain medication or have you wear a cast to protect the heel bone. Surgery is available for extreme cases.
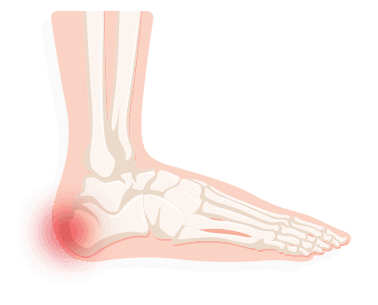
Heel Spurs
Plantar fascia is the tissue forming the natural arch of a foot which can become swollen. Unfortunately this usually leads to heel spurs, a bone that has hooked at the heel. X-rays diagnose the problem and the first plan to relieve the pain is to sit and rest as much as possible, while icing the affected area. Take over the counter anti-inflammatory, stretch before working out, and try shoe pads. It is also important to wear shoes with good arch support and a cushioned sole. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT), injections and surgery are available for serious cases.
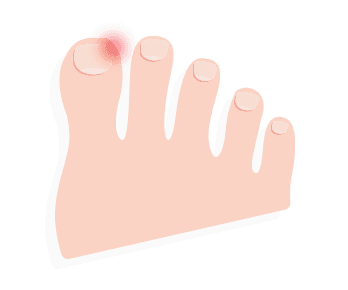
Ingrown Toenail
While this is more focused on the toenail rather than the entire foot, it can be quite uncomfortable and lead to infections. To treat ingrown toenails, you will want to not only keep the area as clean as possible by soaking the foot in warm water around four times a day, but also wedging a piece of gauze in between the nail and wet skin. If conditions doesn’t improve, then it’s time to see a podiatrist for expert treatment.
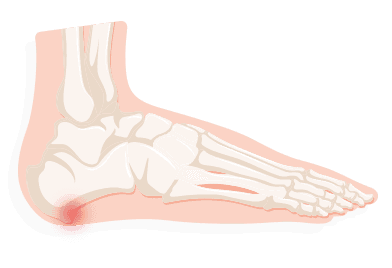
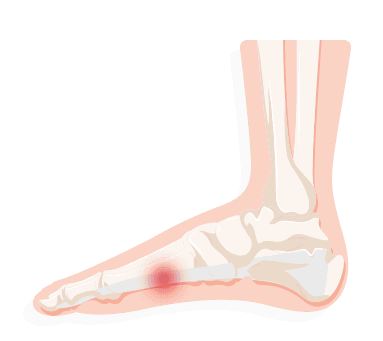
Metatarsalgia
Metatarsalgia occurs at the ball of the foot and features a sharp or burning ache that increases in severity when standing or running. Common complaints are numbness, tingling and shooting pains. As this is not a serious issue, resting, wearing more comfortable shoes, and propping and soaking feet should alleviate the problem in time and wearing footwear designed with a high, wide toe box and a rocker sole. Taking painkillers and icing your feet can also help alleviate pain.
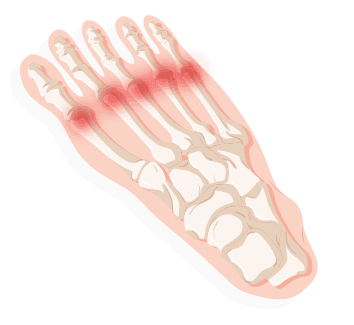
Morton’s neuroma
Similar to Metatarsalgia, only Morton’s neuroma is a benign growth of nerve tissue frequently found between the third and fourth toes. Pain symptoms include a burning sensation, tingling, or numbness between the toes and in the ball of the foot. The pain severity is the same, though in this case the body increases skin tissue around the nerve. Generally speaking, in response to injury or bad footwear, Morton’s neuroma should clear up naturally with basic treatment, though severe cases can lead to injection therapy or surgery. Usually, women experience this more often because it often results from wearing high heels or tight shoes excessively.
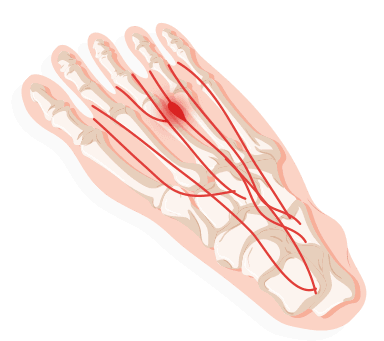
Plantar Fascitis
The plantar fascia is a thin, web-like ligament that connects your heel to the front of your foot. It supports the arch of your foot and helps you walk. When the area is injured or strained, the foot begins to be inflamed and weak. Causes include high arches, flat feet, obesity, poor footwear and cold muscles. This can make common activities such as standing, running and walking very difficult. Common treatments include new shoes, arch supports, physical therapy, icing feet and in severe cases the use of steroids or splints or surgery.
Pronation
When walking, a neutral foot absorbs the weight of the body and the shock from the ground and distributes it evenly throughout the whole foot. In pronation, the foot rolls forwards and outwards so far that it strains and stretches the arch ligaments of the foot and it flattens. Children with pronation can learn exercises, have arch supports, or sleep with braces that can strengthen their muscles and teach them to walk correctly. Adults can elect to use specially made shoes, arch supports and padded soles to alleviate some of the effects.
Sesamoiditis
Sesamoids are bones that do not attach to other bones; rather they connect to tendons or are embedded within muscle tissue. When sesamoids break or the tissue or tendon around the bone becomes inflamed, tendinitis in the form of sesamoiditis can appear. Pain usually centers under the big toe, making bending or straightening difficult. A physical examination and X-rays may diagnose the problem and treatment usually includes resting, anti-inflammatory medication, and use of a specialized shoe or a pad.
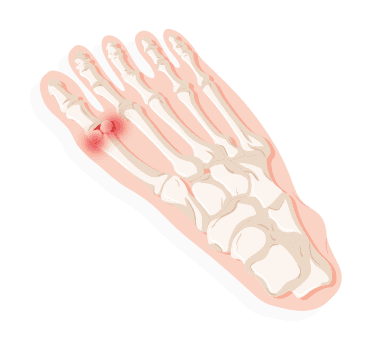
Tailor’s Bunions
Also known as Bunionettes, Tailor’s Bunions are less common than general bunions but are caused by the same factors. It is a prominence of the fifth metatarsal bone at the base of the little toe. Family genetics, rubbing, and natural development are all factors. Symptoms include inflammation, pain, and redness, especially with tight fitting footwear. Generally very obvious, diagnosis can happen visually without X-rays. Changes in shoes, adding padding, and taking anti-inflammatory medication should relieve the problem, though injections or surgery may be considered.
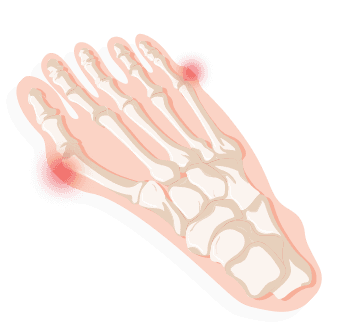
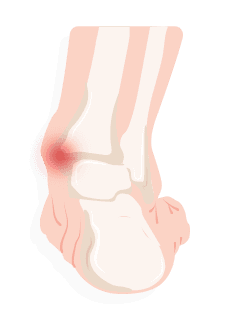
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome is when the nerve between the ankle and the foot is compressed. Causes include flat feet, swollen tendons, sprained ankles and diabetes. Numbness and shooting pain have been reported as complications. To diagnose, the doctor will test the nerve and possibly take images within the area to further examine the problem. Resting, icing, anti-inflammatory medicine, physical therapy and new footwear should help, though surgery is the best available option.
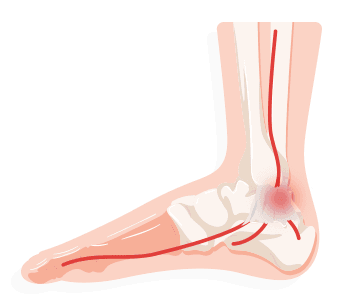
Tendonitis
If your tendons are feeling irritated, it’s likely that they are inflamed and you have tendinitis. To treat this, you will want to give your feet as much rest as possible, while taking pain relievers. Usually, surgery is not needed to fix the issue, but steroid injections may help depending on the severity.
Tinea Pedis (Athlete’s Foot)
Athlete’s foot is generally found around foot soles, in between toes and toenails. If touching the affected area, it is important to immediately rewash hands, as it can spread to the hands and groin as well. Common symptoms include itching, redness, burning and flaking or cracking skin at the bottom of feet. Antifungal creams should clear up the affected problem and keeping skin clean and dry should prevent tinea from coming back.
There are many types of podiatry ailments out there, and it can be hard to determine which one you might have. The simplest and safest way to diagnose any type of foot pain is to seek a medical professional opinion as early as possible. However, there are at-home treatments that can be performed to improve the conditions. Mild foot pains may take a while to recover at home, while the more severe ones will most likely benefit from a Podiatrist’s attention.



